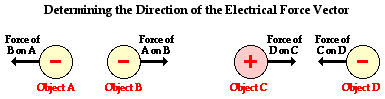
Coulomb's law, developed by Charles Augustin de Coulomb, may be stated as follows:
The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two points electric charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of each charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges.
The magnitude of the electrostatic force between two points electric charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of each charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges.
Electrical force also has a magnitude or strength. Like most types of forces, there are a variety of factors which influence the magnitude of the electrical force. Two like-charged balloons will repel each other and the strength of their repulsive force can be altered by changing three variables. First, the quantity of charge on one of the balloons will affect the strength of the repulsive force. The more charged a balloon is, the greater the repulsive force. Second, the quantity of charge on the second balloon will affect the strength of the repulsive force. Gently rub two balloons with animal fur and they repel a little. Rub the two balloons vigorously to impart more charge to both of them, and they repel a lot. Finally, the distance between the two balloons will have a significant and noticeable affect upon the repulsive force. The electrical force is strongest when the balloons are closest together. Decreasing the separation distance increases the force. The magnitude of the force and the distance between the two balloons is said to be inversely related.
The quantitative expression for the affect of these three variables on electric force is known as Coulomb's law. Coulomb's law states that the electrical force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of the quantity of charge on the objects and inversely proportional to the square of the separation distance between the two objects. In equation form, Coulomb's law can be stated as
where:
F=is the magnitude of the force exerted,
q1=is the charge on one body,
q2=is the charge on the other body,
r=is the distance between them,
F=is the magnitude of the force exerted,
q1=is the charge on one body,
q2=is the charge on the other body,
r=is the distance between them,
k=9.0 x 109 N • m2 / C2 (constant)